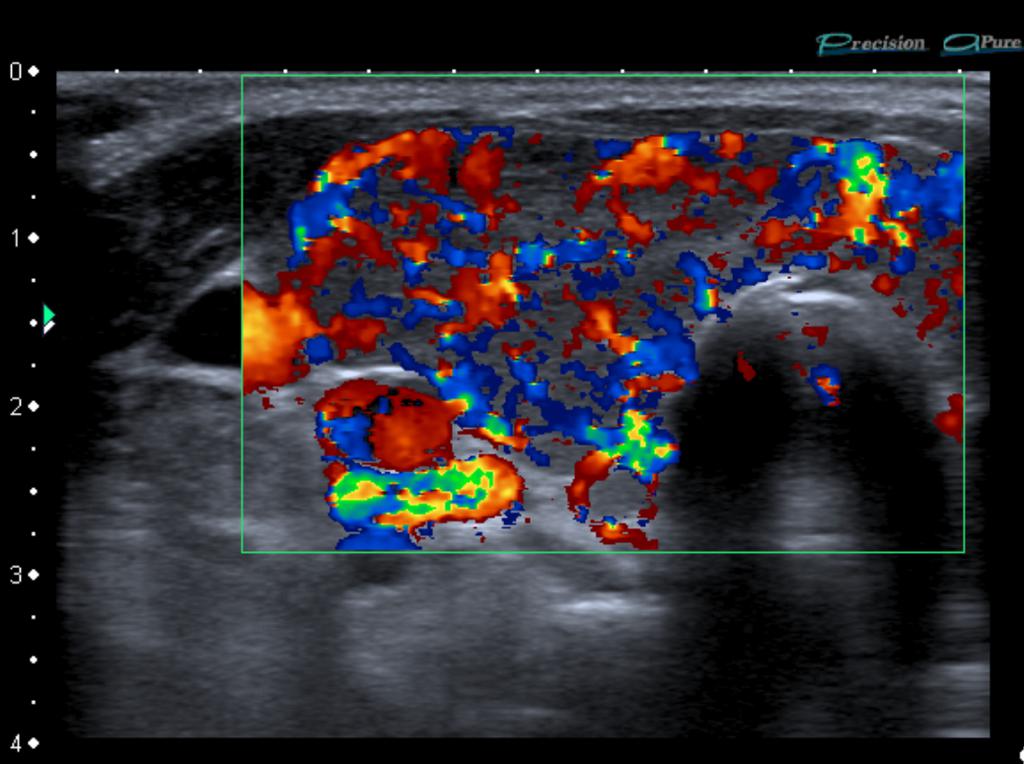
What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound . With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter.
from www.pinkybone.com
Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow;
Thyroïde PinkyBone
What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ].
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Hashimotos Thyroiditis Ultrasound What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.pinterest.com
Pin on u/s studies What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity,. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.pinterest.com
Graves Disease >>> Click image for more details. Graves disease What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody). What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From doctorvisit.netlify.app
Thyroid cancer ultrasound colors doctorvisit What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.youtube.com
Grave's Disease Sonography YouTube What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From symptomclinic.com
Graves' Disease Symptoms Causes Treatment & Role of Hyperthyroidism What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity,. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From thyroidultrasoundwagusami.blogspot.com
Thyroid Ultrasound Graves Disease Thyroid Ultrasound What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. Autoantibodies (thyroid. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.dermatologyadvisor.com
Skin Manifestations of Thyroid Disorders A Review Dermatology Advisor What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. A thyroid. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From polymedlab.ph
THYROID ULTRASOUND Polymed Lab What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.pinterest.com
Ophthalmologist Rochester NY Eye Surgeon Envision Eye & Aesthetics What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From mungfali.com
Thyroid Eye Disease Surgery What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.svuhradiology.ie
Graves disease Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From rfaforlife.com
Why do I have Thyroid Nodules? RFA For Life Blog What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.onehealthcare.co.uk
Thyroid Disorders Mr Robert Hone, ENT Surgeon One Ashford Hospital What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.dailymeded.com
Graves Disease Hyperthyroidism Complete Overview What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound A thyroid gland impacted by graves’ disease is often enlarged and may have increased blood flow; With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.vrogue.co
What Is Graves Disease Thyroid Advisor vrogue.co What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy are the typical. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.lceyes.com
What is thyroid eye disease and can it be treated? Lowcountry Eye What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected graves’ disease. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, followed by toxic multinodular goiter. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. A diffuse goiter with high vascularization at neck ultrasound and high uptake at thyroid scintigraphy. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.
From www.youtube.com
Case 70 Study Hashimotos thyroiditis Dr AHMED ESAWY YouTube What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound With superior sensitivity in the detection and characterization of thyroid nodules, malignant lymph nodes and recurrent thyroid cancer,. Rarer causes include an autonomously functioning thyroid adenoma and thyroiditis [ 3 ]. Thyroid ultrasound demonstrates an enlarged gland that has characteristic echogenicity, easily distinguishable from adjacent muscular. Autoantibodies (thyroid peroxidase [tpo] and/or thyroid receptor antibody) were tested in patients with suspected. What Does A Graves Disease Thyroid Look Like On Ultrasound.